SMEAR TEST
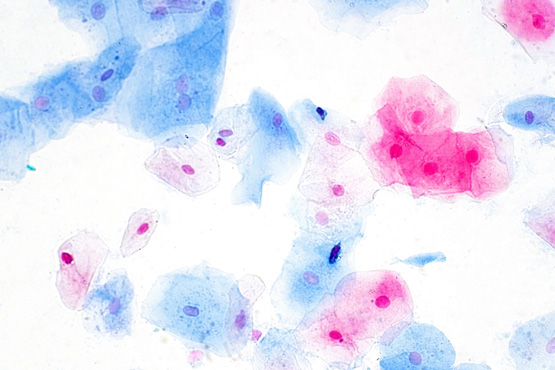
What is a Smear Test?
A smear test is a screening test used for the early detection of cervical cancer and its precursors. In this test, a gynecologist collects cell samples from the cervix using a special brush or spatula. These samples are then examined in a laboratory.
Why is a Smear Test Done?
The smear test is primarily used for cervical cancer screening. It can also assist in identifying sexually transmitted infections.
How is a Smear Test Done?
The patient lies on an examination table in a gynecological examination position. The gynecologist or nurse uses an instrument called a speculum to collect cell samples from the cervix. The samples taken by the smear method from the cervix are sent to the laboratory for pathological examination.
Is a Smear Test Difficult?
Smear tests are generally safe and straightforward. However, some women may experience mild discomfort or cramping during or after the test. Occasionally, there can be slight bleeding in the form of spotting after the test.
Is a Smear Test Painful?
A smear test is a painless procedure. However, there may rarely be mild cramping or pain.
How Often Should a Smear Test Be Done?
According to current guidelines for cervical cancer screening from leading health organizations such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the American Cancer Society (ACS):
Who Should Have a Smear Test?
All women aged 21 and over are recommended to have a regular smear test. This usually includes women up to the age of 65, including postmenopausal women.
When Do Smear Test Results Come Out?
Smear test results typically come out within 4-7 days. The results can be normal, abnormal, or inconclusive. Abnormal results indicate cellular changes in the cervix. However, this does not always mean cancer. Further testing may be required.
What Can Come Out in Smear Test Results?
Smear test results are usually evaluated in a series of categories, depending on how abnormal the cells are. Results are usually reported as follows:
What Should Be Done If the Smear Test Result Is Abnormal?
An abnormal smear test result usually requires further testing. These tests include a colposcopy or a biopsy from the cervix.
Which Diseases Can Be Diagnosed With a Smear Test?
The smear test is primarily used to detect cervical cancer and precursor lesions. It can also indicate sexually transmitted infections such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
Is It Possible to Prevent Cervical Cancer With a Smear Test?
Yes, the smear test is an effective tool for the early diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. It can detect and treat precancerous cell changes.
Should a Smear Test Be Done During Pregnancy?
It is generally safe to have a smear test during pregnancy, and in most cases, it is recommended that the routine smear test continues even after you find out you are pregnant.
However, according to guidelines published by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), a smear test should routinely be done every 3-5 years. Therefore, if a woman's time for a smear test has not come during pregnancy, the test is usually postponed until after childbirth.
However, it is always important to consider individual situations. If a woman has never had a smear test before pregnancy, this test can be done during pregnancy. Moreover, if a woman has a history of HPV infection or abnormal smear test, a smear may need to be done during pregnancy.
Should a Smear Test Be Done After Menopause?
Yes, it is generally recommended that all women, including postmenopausal women, have a regular smear test up to the age of 65. After the age of 65, screening can be stopped after two consecutive normal smear tests.
What Is the Price of a Smear Test?
We cannot publish the prices of smear tests on the site due to the rules of the Ministry of Health. Patients who want to get price information can call us at 0505 260 72 38 and 0 850 490 14 78 or contact us by message. Most health insurance covers the smear test. You can benefit from your private insurance in our clinic.
What should you be aware of before or after a smear test?
Before a smear test, it's generally recommended that you abstain from sexual intercourse and avoid using products like vaginal creams, foams, or lotions. These could affect the test results. After the test, you might experience light bleeding or spotting, but this is usually brief and mild. If any pain, discomfort, or bleeding continues, you should consult your doctor.
This article may also interest you
Every woman with high-risk HPV virus types should have a colposcopy, there is no need for anesthesia during the colposcopy procedure.
Read more

 TR
TR EN
EN