GENITAL WARTS
What is Genital Warts?
Genital warts are a contagious disease caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), usually transmitted sexually. They often appear as wart-like growths or blisters around the genitals and anus.
What Causes Genital Warts?
There are over 300 types of HPV, but around 40 types preferentially cause infection in the genital area. HPV types 6 and 11 are responsible for approximately 80% of genital warts.
What Are the Symptoms of Genital Warts?
Symptoms of genital warts usually manifest as wart-like growths, blisters, or bumps around the genitals or anus. There can sometimes be itching, unpleasant smell, or discomfort.
How Do Genital Warts Spread?
Genital warts are most commonly (80% of cases) transmitted through sexual contact such as oral, anal, and vaginal sex. Transmission through non-sexual contact has been reported but is much less common. Examples include shared use of razors or wax, rapid contact with the same surface, gynecological examinations, and transfer from hands to the genital area. The virus can also be passed from mother to baby during birth (vertical transmission).
How Are Genital Warts Treated?
The goal in treating genital warts is to effectively destroy the warts. This destruction can be achieved through several methods, with laser therapy being at the forefront.
What Are the Complications of Genital Warts?
In some cases, genital warts can cause pain, discomfort, or problems during sexual intercourse. Also, certain types of HPV, such as HPV type 16 and HPV type 18, can increase the risk of cervical cancer.
What Should Be Done to Prevent the Spread of Genital Warts?
Genital warts tend to spread from their location to the side (referred to as horizontal spread), and most often this is caused by improper hair removal behaviors by patients. Scratching and breaking off warts, causing them to bleed, shaving them off with a razor, ripping them off with wax, and irritating healthy skin and warts with hair removal creams can spread the existing viruses and cause warts to multiply. Therefore, if you have a wart, do not break it off. Remove the hair in your genital area with scissors or a shaver, without irritating your skin. And quickly get a checkup from a doctor specializing in warts. Remember that hundreds of new warts can form within months from improper handling of just one wart.
How Is the Diagnosis of Genital Warts Made?
Genital warts are usually diagnosed by an examination performed by a healthcare professional. Sometimes a biopsy or HPV DNA test may be required. The HPV test determines both the presence and type of HPV. It is important to identify the type of HPV because knowing that we are dealing with high-risk types is crucial to determine our treatment and monitoring strategies.
What Is the Relationship Between Genital Warts and HPV?
There are over 300 types of Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Among these types, 40 tend to particularly affect the genital area. HPV Type 6 and HPV Type 11, only two of these 40 types, make up 80% of genital warts. However, this information should not be a relief. Tests show that there is a 12% chance of encountering high-risk HPV types along with low-risk HPV types. Therefore, do not be mistaken that genital warts could be low-risk and do not hesitate to have an HPV test periodically. A conscious and proactive approach is vital to prevent the potential serious consequences of HPV.
What Is the Relationship Between Genital Warts and Sexually Transmitted Diseases?
Genital warts are one of the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), and the transmission methods of these diseases are generally similar. Moreover, the presence of an STD increases the potential to be concurrent with other sexually transmitted diseases. Besides, it has been observed that other STDs such as ureaplasma, mycoplasma, herpes, and trichomonas may also be present in individuals carrying the human papilloma virus (HPV). This situation requires individuals with HPV to take tests like the STD 10 test, which simultaneously diagnoses numerous sexually transmitted diseases.
Are There Different Symptoms of Genital Warts in Women and Men?
The symptoms of genital warts are similar in both women and men, but the locations where the symptoms appear may vary. In men, warts can be seen around the penis, scrotum, or anus, while in women they can be seen around the vulva, cervix, or anus.
What Is the Effect of Genital Warts on Pregnancy?
Pregnancy is a period that suppresses the immune system, thus genital warts can multiply during this time. New warts that were not normally present may appear. Also, genital warts tend to grow during pregnancy. Genital warts do not harm or infect the unborn baby. If transmission is to occur, it can occur during birth, but this risk is not very high. If there are active wart lesions inside the vagina, cesarean delivery may be preferred as the birth method. Pregnant women without active warts can give birth vaginally. Genital warts can be treated during pregnancy using appropriate methods. HPV vaccination is not preferred during pregnancy. The HPV vaccine can be administered safely during the breastfeeding period.
What Precautions Should Be Taken to Prevent the Spread of Genital Warts During Sexual Intercourse?
Genital warts multiply with a ping-pong effect among couples who are not vaccinated and do not use condoms. This is because a virus transfer occurs between partners in each intercourse, causing reinfection. It's important to use condoms during sexual intercourse to prevent the spread of genital warts. Another important point is that both the woman and the man should be vaccinated together. The immunity of both partners reduces the transmission of the HPV virus between the couple and decreases the viral load in the genital area.
What Is the Likelihood of Genital Warts Recurring?
Even after a certain treatment process, genital warts carry a risk of recurrence. This likelihood of recurrence may vary depending on the treatment method used, whether patients continue their risky sexual habits, their smoking habits, and whether or not they have received the HPV vaccine.
In a study conducted on patients diagnosed with genital warts for the first time, the cryotherapy method was applied. It was observed that in 48.5% of the patients who continued to smoke, did not use condoms, and did not get the HPV vaccine, the warts recurred three months after the treatment. If this group of patients continues their risk-involving behaviors, it is stated that the warts recur 4-6 times within a year.
What Are the Methods of Protection from Genital Warts?
The HPV vaccine and using condoms during sexual intercourse are the best ways to prevent genital warts. It is possible to protect against warts with 2 doses of HPV vaccine to be administered at 0 and 6 months for ages 9-14; and 3 doses of HPV vaccine to be administered at 0-2-6 months from the age of 15.
Can I Get Completely Rid of Genital Warts?
The treatment of genital warts varies from person to person. While some people respond quickly to treatment, the process can be longer for others. The important factors here are:
Therefore, for the warts not to recur and for the HPV virus to be expelled from the body, the changes the patient will make in their lifestyle are very important along with correct and effective treatment.
Which specialist should I consult for the treatment of genital warts?
At our Wart Treatment Center located in Silivri, you can get rid of your genital warts under the control of Dr. Associate Professor Eser Ağar, who is an expert in HPV and Wart issues, and get support about the methods to be applied. Our center has a fractional laser, which is the most effective method in the treatment of genital warts. At our center, you can get laser wart treatment, get the HPV vaccine, and have your periodic checks. Even if you forget your periodic controls, we follow up and make reminders by phone.
Treatment of genital warts requires both the male and female partner to be treated together. Both male and female patients' genital wart treatments are performed at our center.
What are the prices for Genital Wart Treatment?
Genital wart treatment prices vary according to the prevalence of warts, their sizes, and the anesthesia to be applied. Our treatment fees are not hidden. You can reach us at 0505 260 72 38 and 0 850 490 14 78 to get information about the treatment process and prices from our staff who are experts in warts.
This article may also interest you
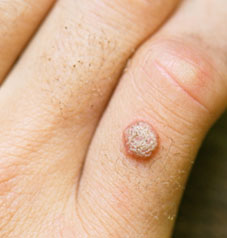
Hand warts are small, hard, raised lesions that occur in the upper layer of the skin, usually on the palm or fingers.
Read more

 TR
TR EN
EN